Inqscribe 2 1 Serial Port
Information About the Cisco 1-, 2-, and 4-port Serial Network Interface Modules The Cisco 1-port, 2-port, and 4-port Serial Network Interface Modules (NIMs) are multi-protocol synchronous serial NIMs supported on the Cisco 4400 Series ISRs. The Cisco 1-, 2-, and 4-port Serial NIMs expand the capabilities of the router to provide connectivity for synchronous interfaces in a wide range of applications including up to 8Mbps date rate for high speed high-level data link control (HDLC). These capabilities can be utilized as Point-to-Point Cisco HDLC WAN interface or frame relay interface.
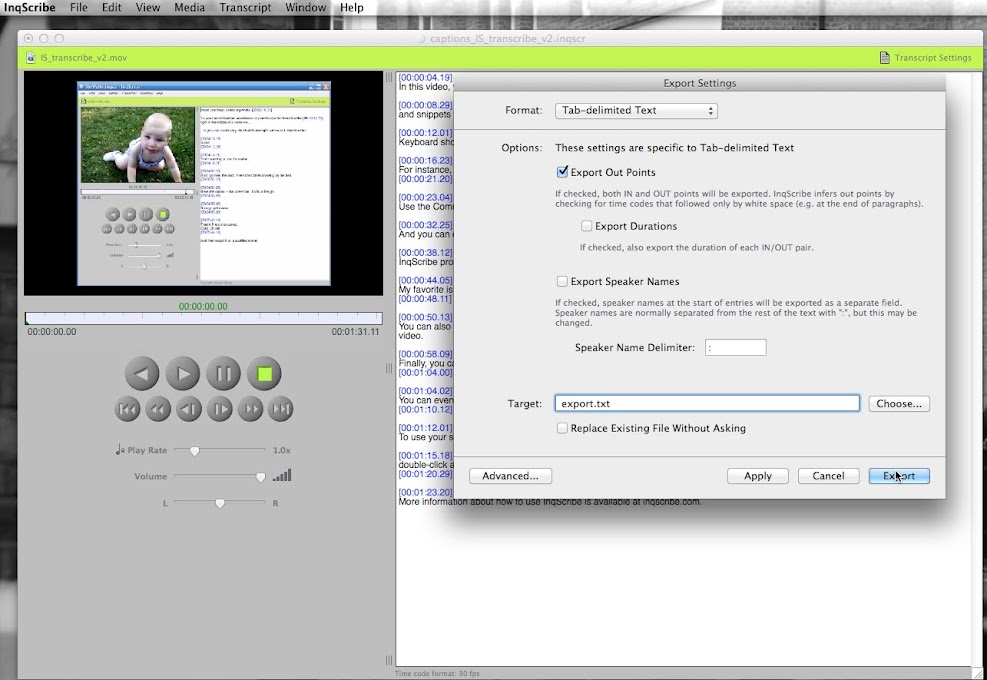
4.1.1 Activating Shortcuts. When InqScribe launches, keyboard shortcuts are turned on by default. If you need to turn shortcuts off, you can use the Edit >Enable Shortcuts menu item. 4.1.2 Managing Shortcuts. InqScribe's default settings include two shortcuts. Just press the button or pedal on the device to set the trigger.

Gta San Andreas Zombie Attack Mod Download more. The Cisco 1-, 2-, and 4-port Serial NIM software is capable of anti-counterfeit protection and provides periodic system status information. The Cisco 1-, 2-, and 4-port Serial NIMs have their own serial communication controllers (SCCs) and they do not rely on the host platform for SCCs.
For more information on the Cisco 1-, 2-, and 4-port Serial NIM LED and hardware features, see the Hardware Installation Guide. Table 1 Cisco 1-port, 2-port, and 4-port Serial HWICs. Cyclic Redundancy Checking Cyclic redundancy checking (CRC) is an error-checking technique that uses a calculated numeric value to detect errors in transmitted data. All the Serial HWIC interfaces use a 16-bit frame check sequence (FCS) CRC by default. The sender of a data frame calculates the FCS. The sender appends the FCS value to the message before sending a frame.The receiver recalculates the FCS and compares its calculation to the FCS from the sender. If there is a difference between the two calculations, the receiver assumes that a transmission error occurred and sends a resend request to the sender.
See the for configuring CRC. Timing Signals The Cisco 1-, 2-, and 4-port Serial NIM interfaces support both the data terminal equipment (DTE) and data communication equipment (DCE) mode, depending on the mode of the compact serial cable attached to the port. To use a port as a DTE interface, you only need to connect a DTE compact serial cable to the port. When the system detects the DTE mode cable, it automatically uses the external timing signal.
To use a port in DCE mode, you must connect a DCE compact serial cable and set the clock speed with the clock rate configuration command. Vertex Tools Sketchup Crack Keygen. See for setting up a clock rate.
Encapsulation Protocols Encapsulation protocols connect the layer- 2 (link layer) protocols with the layer-3 (network layer) protocols. When traffic crosses a WAN link, the connection needs a layer 2 protocol to encapsulate traffic. The Cisco 1-, 2-, and 4-port Serial NIM interfaces support the High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC), Point-to-point (PPP), and Frame Relay encapsulation protocols. The HDLC protocol, is the router proprietary protocol that decodes proprietary framing used by the routers on the PPP links. The standard PPP protocol supports the PPP links analyzed by the HDLC and can also be utilized for Frame Relay. The standard Frame Relay encapsulation protocol is a versatile and common encapsulation protocol used with Frame Relay.
See to set the encapsulation method. Configuring Optional Features This section provides you the information on configuring options features and the Cisco IOS XE commands required to configure these features: • • • • • • • Enhanced Object Tracking On your serial NIM, you can enable the Enhanced Object Tracking (EOT) feature to consider the carrier-delay timer when tracking the status of an interface.